This study guide is designed to help you prepare effectively for your PHY111 exam by providing a comprehensive set of past questions and detailed answers. Whether you are revising key concepts or practicing problem-solving skills, this guide will enhance your understanding and boost your confidence.
Phy111 past questions and answers 1

Phy111 past questions and answers 2
Question 2: The increase in size or volume of a given mass of substance with a change in temperature is called __________
Options:
- (a) Thermal expansion
- (b) Electrical effect
- (c) Gravitational reaction
- (d) Heat capacity
Solution: The phenomenon where the size or volume of a substance increases when its temperature rises is known as thermal expansion. It is a result of the increased kinetic energy of particles, causing them to move more and occupy more space.
Correct Answer: (a) Thermal expansion
Phy111 past questions and answers 3
Question 3: Another name for area expansivity is __________.
Options:
- (a) Superficial expansivity
- (b) Cubic expansivity
- (c) Linear expansivity
- (d) Area expansivity
Solution: Area expansivity refers to the increase in the surface area of a material with an increase in temperature. It is also called superficial expansivity.
Correct Answer: (a) Superficial expansivity
Phy111 past questions and answers 4
Question 4: Another name for volume expansivity is __________.
Options:
- (a) Cubic expansivity
- (b) Area expansivity
- (c) Linear expansivity
- (d) Volume increase
Solution: Volume expansivity, also known as cubic expansivity, is the increase in volume of a material with an increase in temperature.
Correct Answer: (a) Cubic expansivity
Phy111 past questions and answers 5
Question 5: Two types of volume expansivity in liquids are __________.
Options:
- (a) Apparent cubic expansivity and real cubic expansivity
- (b) Real cubic expansivity and absolute expansivity
- (c) Apparent cubic expansivity and thermal expansivity
- (d) None of the above
Solution: Volume expansivity in liquids can be described by two types: apparent cubic expansivity (which is observed when a liquid expands in a container) and real cubic expansivity (which accounts for the expansion of the liquid alone, without the container).
Correct Answer: (a) Apparent cubic expansivity and real cubic expansivity
Phy111 past questions and answers 6
Question 6: __________ relates hydrostatic pressure to volume strain.
Options:
- (a) Bulk modulus
- (b) Shear modulus
- (c) Compressibility
- (d) Axial modulus
Solution: The bulk modulus is a measure of a substance’s resistance to uniform compression. It relates hydrostatic pressure to the change in volume (volume strain).
Correct Answer: (a) Bulk modulus
Phy111 past questions and answers 7
Question 7: __________ denotes the force exerted on a body.
Options:
- (A) Tensile Stress
- (B) Tensile Strain
- (C) Elasticity Extension
Solution: Tensile stress refers to the force exerted per unit area on a material, which leads to its deformation.
Correct Answer: (A) Tensile Stress
Phy111 past questions and answers 8
Question 8: The most suitable thermometer for measuring temperature between 200°C and 1200°C is __________.
Options:
- (A) Platinum resistance
- (B) Mercury-in-glass
- (C) Thermocouple
- (D) Optical pyrometer
Solution: An optical pyrometer is suitable for measuring high temperatures, especially in the range of 200°C to 1200°C, where other types of thermometers may not be accurate or practical.
Correct Answer: (D) Optical pyrometer
Phy111 past questions and answers 9
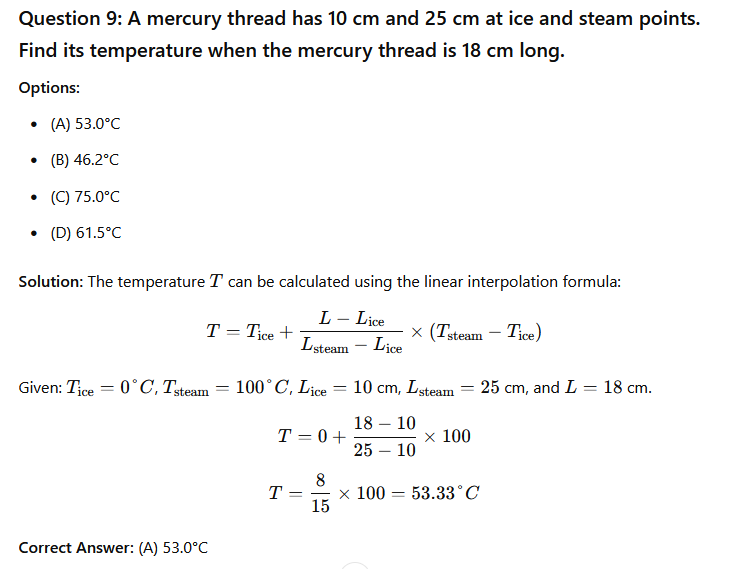
Phy111 past questions and answers 10

Phy111 past questions and answers 11
Question 11: Among the three ways in which heat can be transferred, one of them does not require a material medium. This is __________.
Options:
- (a) Convection
- (b) Conduction
- (d) Radiation
- (d) Thermodynamic
Solution: Heat transfer can occur through conduction, convection, or radiation. Radiation is the only method that does not require a material medium; it can occur through a vacuum.
Correct Answer: (d) Radiation
Phy111 past questions and answers 12
Question 12: A block of copper is heated to an initial temperature and later placed in 0.2 kg of water at 30°C. When thermal equilibrium is attained, the temperature of the mixture is 35°C. How much heat is absorbed by the water? (Take the specific heat capacity of water as 4200 J/kg·K)
Options:
- (A) 8400 J
- (B) 3360 J
- (C) 4200 J
- (D) 5040 J
Solution: The heat absorbed by the water can be calculated using the formula: Q=mcΔTQ = mc\Delta TQ=mcΔT
Where:
- m =0.2kg (mass of water)
- c=4200J/kg.K (specific heat capacity of water)
- ΔT=35°C−30°C =5°C (change in temperature)
Q=0.2×4200×5=4200 J
Correct Answer: (C) 4200 J
Phy111 past questions and answers 13
Question 13: In the determination of specific heat capacity by the method of mixtures, one of these apparatus is used to measure the temperature of the heated object whose specific heat capacity is to be determined.
Options:
- (A) Heater
- (B) Glass rod
- (C) Thermometer
- (D) Felt
Solution: The thermometer is used to measure the temperature of the heated object in the method of mixtures.
Correct Answer: (C) Thermometer
Phy111 past questions and answers 14
Question 14: The three phases of matter are __________.
Options:
- (A) Evaporation, plasma, ice
- (B) Conduction, convection, radiation
- (C) Solid, liquid, gas
- (D) Mass, weight, space
Solution: The three classical phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
Correct Answer: (C) Solid, liquid, gas
Phy111 past questions and answers 15
Question 15: The S.I. unit of heat capacity is __________.
Options:
- (A) kg
- (B) J
- (C) J·kg⁻¹
- (D) J·kg⁻¹·K⁻¹
Solution: The S.I. unit of heat capacity is joules per kilogram per kelvin (J·kg⁻¹·K⁻¹).
Correct Answer: (D) J·kg⁻¹·K⁻¹
Phy111 past questions and answers 16
Question 16: Newton’s 3rd law refers to action and reaction forces; the forces always occur in pairs and __________.
Options:
- (a) Act on the same object
- (b) Act at right angles
- (c) Never act on the same object
- (d) Move a body
Solution: Newton’s 3rd law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. These forces act on different objects, not the same object.
Correct Answer: (c) Never act on the same object
Phy111 past questions and answers 17
Question 17: Mass and weight __________.
Options:
- (a) Both have the same units
- (b) Both measure inertia
- (c) Both have different units
- (d) Represent gravity
Solution: Mass is measured in kilograms (kg), and weight is a force measured in newtons (N). Thus, they have different units.
Correct Answer: (c) Both have different units
Phy111 past questions and answers 18
Question 18: __________ deals with the motion of bodies with reference to the force.
Options:
- (a) Mechanics
- (b) Electromagnetism
- (c) Dynamics
- (d) Motion
Solution: Dynamics is the branch of mechanics that deals with the motion of bodies and the forces acting upon them.
Correct Answer: (c) Dynamics
Phy111 past questions and answers 19
Question 19: __________ initiated the study of dynamics.
Options:
- (a) Newton
- (b) Faraday
- (c) Galileo
- (d) Boyle
Solution: Galileo is often credited with initiating the study of dynamics, laying the groundwork for Newton’s laws of motion.
Correct Answer: (c) Galileo
Phy111 past questions and answers 20
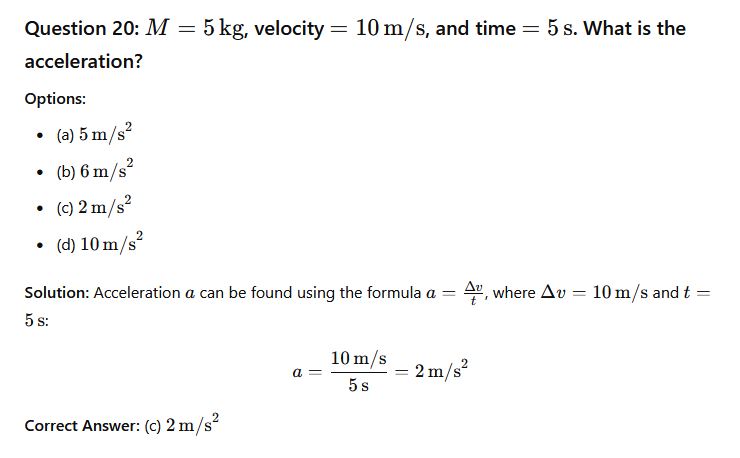
Phy111 past questions and answers 21
Question 21: For a cone in unstable equilibrium, the center of gravity is __________ if displaced by a small force applied on it.
Options:
- (A) Lowered
- (B) Increased
- (C) Varied
- (D) Unchanged
Solution: In unstable equilibrium, the center of gravity is raised when the object is displaced by a small force, leading to the object toppling over.
Correct Answer: (B) Increased
Phy111 past questions and answers 22
Question 22: __________ is responsible for acceleration in rotational motion.
Options:
- (A) Torque
- (B) Force
- (C) Work
- (D) Speed
Solution: Torque is the rotational equivalent of force and is responsible for causing angular acceleration in rotational motion.
Correct Answer: (A) Torque
Phy111 past questions and answers 23

Phy111 past questions and answers 24
Question 24: An example of a torque on a body is when a football is being kicked __________.
Options:
- (A) Obliquely
- (B) Linearly
- (C) Forcefully
- (D) Vertically
Solution: Torque is the rotational effect of a force applied at a distance from the axis of rotation. When a football is kicked obliquely, it tends to spin, indicating the presence of torque.
Correct Answer: (A) Obliquely
Phy111 past questions and answers 25

Phy111 past questions and answers 26
Question 26: Using the fundamental quantities M, L and T, derive the dimension of the pressure gradient.
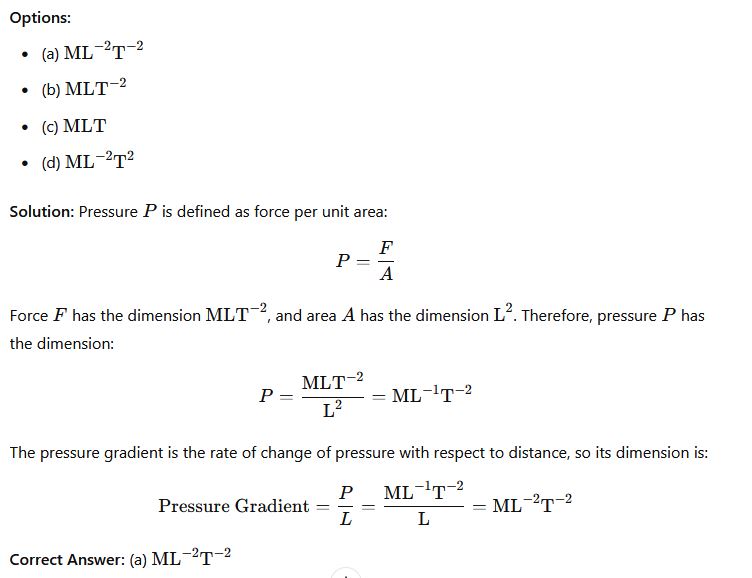
Phy111 past questions and answers 27
Question 27: Write the dimension of the coefficient of attenuation.

Phy111 past questions and answers 28
Question 28: What is the dimension of the impulse of a force?
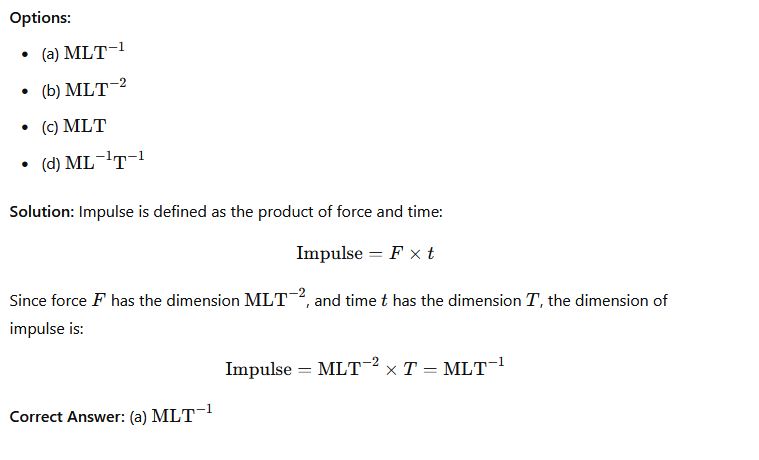
Phy111 past questions and answers 29
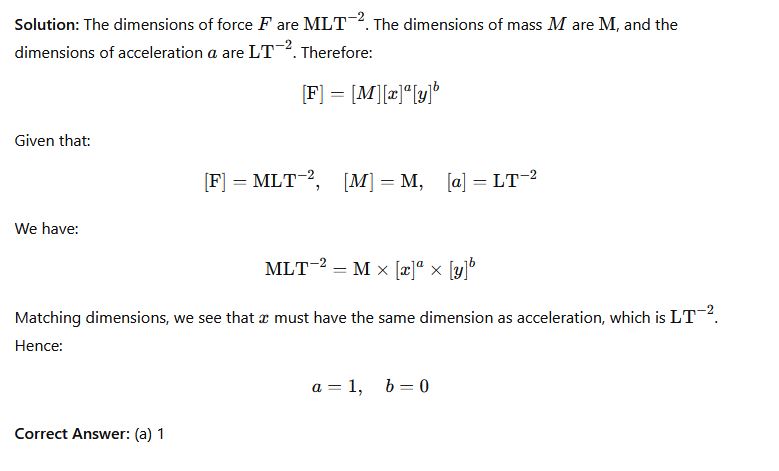
Question 29: Given the equation F = Mx^ay^b, where F is force, M is mass, and a is linear acceleration, use dimensional analysis to find the value of x
Options:
- (a) 1
- (b) 0
- (c) 2
- (d) -1
Phy111 past questions and answers 30
Question 30: i.i=j.j=k.k is __________.
Options:
- (a) Vector
- (b) Unity
- (c) Unit Vector
- (d) Perpendicular
Solution: The dot product of any unit vector with itself is 1 (unity).
Correct Answer: (b) Unity
Phy111 past questions and answers 31
Question 31: If a=i+j−3k and b=3i+3j+k Find a+ b
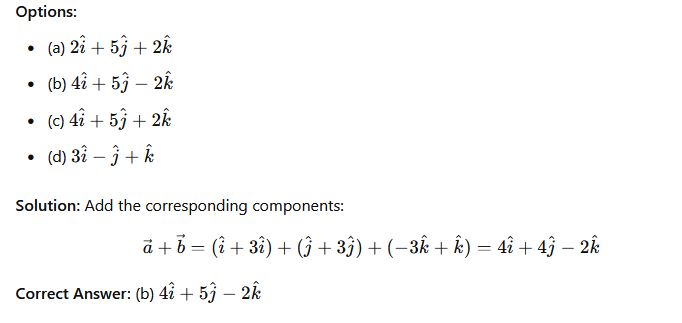
Phy111 past questions and answers 32
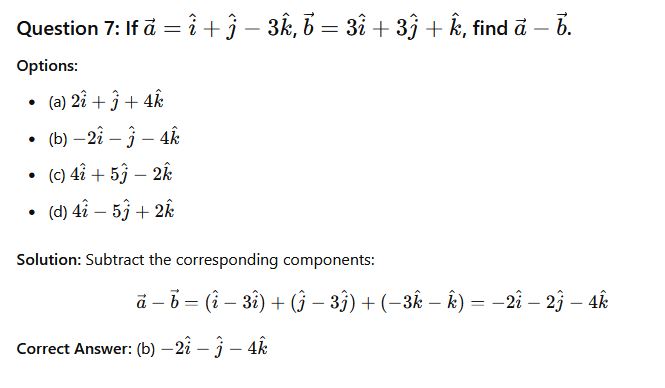
Phy111 past questions and answers 33
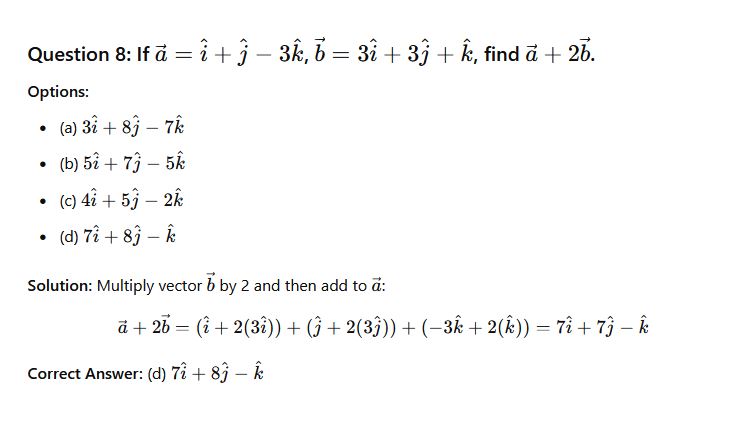
Phy111 past questions and answers 34
Question 34: The statement of the First Law of Thermodynamics can be expressed mathematically as:
- Options:
- (a) dQ=dU−dW
- (b) dQ=dW+dU
- (c) dU=dQ+dW
- (d) dW=dU+dQ
Solution: The First Law of Thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system (dU) is equal to the heat added to the system (dQ) minus the work done by the system (dW). Mathematically, it is expressed as:dU=dQ−dW
However, since work done by the system is typically written as dWdWdW, and work done on the system is taken as positive, the correct form for most practical applications is:dQ=dU+dW
Correct Answer: (b) dQ=dW+dU
Phy111 past questions and answers 35
Question 35: The way of reducing the effect of frictional force in machinery is:
- Options:
- (a) Vulcanizing
- (b) Ball bearing
- (c) Lubrication
- (d) Grazing
Solution: The most effective ways to reduce friction in machinery include using ball bearings and lubrication. Lubrication reduces the friction between moving parts by creating a film of liquid or grease. Ball bearings reduce friction by providing rolling motion instead of sliding.
Correct Answer: (c) Lubrication
Phy111 past questions and answers 36
Question 36: What is the weight of a 50kg astronaut on the moon if the acceleration due to gravity is 1.7m/s²?

Phy111 past questions and answers 37
Question 37: A revolver of mass 3kg releases a bullet of mass 2kg at a speed of 60m/s. What is the revolver’s speed of recoil?
- Options:
- (a) 40 m/s
- (b) 90 m/s
- (c) 300 m/s
- (d) 60 m/s
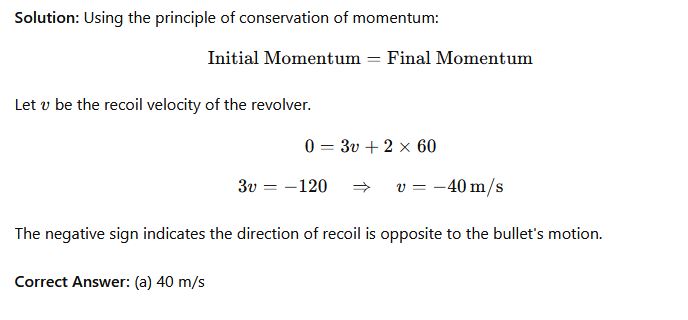
Phy111 past questions and answers 38
Question 38: Impulse is defined as:
- Options:
- (a) Force × Time
- (b) Force/Time
- (c) Force × Area
- (d) Pressure × Time
Solution: Impulse is the product of force and the time interval during which the force acts:Impulse=Force×Time
Correct Answer: (a) Force × Time
Phy111 past questions and answers 39
Question 39: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is:
- Options:
- (a) Newton’s Third Law of Motion
- (b) Newton’s Second Law of Motion
- (c) Faraday’s Law of Induction
- (d) Ampere’s Law
Solution: This statement is a direct expression of Newton’s Third Law of Motion.
Correct Answer: (a) Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Phy111 past questions and answers 40
Question 40: The fractional increase in volume per unit increase in pressure is termed:
- Options:
- (a) Bulk Modulus
- (b) Compressibility
- (c) Young’s Modulus
- (d) Shear Modulus
Solution: Compressibility is defined as the fractional change in volume per unit increase in pressure.
Correct Answer: (b) Compressibility
Phy111 past questions and answers 41
Question 41: What will be the value of 30 rev/min in rad/s?

Boosting Your Knowledge with Practice Quizzes: Your Path to Success
To get the most out of your study sessions, make quiz practice a regular part of your routine. Set aside a few minutes each day to tackle a quiz, and watch as your understanding deepens and your scores soar.
Remember, every quiz you take is a step closer to achieving your goals. Whether you’re preparing for an exam, enhancing your knowledge, or simply testing your understanding, practice quizzes are your gateway to success. So, take the leap—start quizzing today, and empower yourself to reach new heights!






