This study guide is tailored to support your CHM111 exam preparation by offering a thorough collection of past questions with detailed answers. Whether you’re revisiting key concepts or sharpening your problem-solving techniques, this guide will strengthen your understanding and build your confidence.
CHM111 past questions and answers 1
Which of the following particles is not found in the nucleus of an atom?
- A) Proton
- B) Neutron
- C) Electron
- D) Positron
Answer: C) Electron
Explanation: The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons. Electrons are found in orbitals surrounding the nucleus.
CHM111 past questions and answers 2
Which of the following ions has the same electron configuration as neon?
- A) Na+
- B) Cl-
- C) O2-
- D) Mg2+
Answer: A) Na+
Explanation: Neon has the electron configuration 1s² 2s² 2p⁶. The Na+ ion, after losing one electron, also has this configuration.
CHM111 past questions and answers 3
Q3. How many grams of H₂O are produced when 4.00 g of hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen gas according to the balanced equation: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O?
- A) 18.0 g
- B) 36.0 g
- C) 72.0 g
- D) 8.00 g
Answer: B) 36.0 g
Explanation: 4.00 g of H₂ corresponds to 2 moles (since molar mass of H₂ = 2 g/mol). According to the balanced equation, 2 moles of H₂ produce 2 moles of H₂O, which is 36 g.
CHM111 past questions and answers 4
Q4. What is the empirical formula of a compound that contains 40% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen, and 53.3% oxygen by mass?
- A) CHO
- B) CH₂O
- C) C₂H₄O₂
- D) C₃H₆O₃
Answer: B) CH₂O
Explanation: Converting percentages to moles, the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in the compound is 1:2:1 for C:H, giving CH₂O.
CHM111 past questions and answers 5
In a combustion reaction, which substance is always a product?
- A) Carbon monoxide
- B) Water
- C) Nitrogen
- D) Methane
Answer: B) Water
Explanation: Combustion of hydrocarbons always produces carbon dioxide and water.
CHM111 past questions and answers 6
Which of the following is not a type of chemical reaction?
- A) Synthesis
- B) Decomposition
- C) Single replacement
- D) Evaporation
Answer: D) Evaporation
Explanation: Evaporation is a physical change, not a chemical reaction.
CHM111 past questions and answers 7
Which gas law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant pressure?
- A) Boyle’s Law
- B) Charles’s Law
- C) Avogadro’s Law
- D) Gay-Lussac’s Law
Answer: B) Charles’s Law
Explanation: Charles’s Law states V ∝ T at constant pressure.
CHM111 past questions and answers 8
What volume will 2.0 moles of an ideal gas occupy at STP?
- A) 22.4 L
- B) 44.8 L
- C) 11.2 L
- D) 2.0 L
Answer: B) 44.8 L
Explanation: At STP, 1 mole of an ideal gas occupies 22.4 L, so 2 moles will occupy 44.8 L.
CHM111 past questions and answers 9
Which of the following processes is exothermic?
- A) Melting ice
- B) Boiling water
- C) Combustion of methane
- D) Evaporation of alcohol
Answer: C) Combustion of methane
Explanation: Combustion releases energy in the form of heat, making it an exothermic process.
CHM111 past questions and answers 10
The enthalpy change for a reaction is positive. What does this indicate about the reaction?
- A) The reaction is exothermic.
- B) The reaction is endothermic.
- C) The reaction is spontaneous.
- D) The reaction is at equilibrium.
Answer: B) The reaction is endothermic.
Explanation: A positive enthalpy change indicates that the reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings.
CHM111 past questions and answers 11
What is the electron configuration of a chlorine atom?
- A) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁵
- B) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶
- C) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁴
- D) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s¹ 3p⁶
Answer: A) 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁵
Explanation: Chlorine has 17 electrons. This configuration shows that chlorine has a total of 17 electrons, with the distribution across the different orbitals as follows:
- 1s^2: 2 electrons in the 1s orbital
- 2s^2: 2 electrons in the 2s orbital
- 2p^6: 6 electrons in the 2p orbitals
- 3s^2: 2 electrons in the 3s orbital
- 3p^5: 5 electrons in the 3p orbitals
This leaves chlorine with 7 valence electrons in its outermost shell (3s^2 3p^5), making it one electron short of a full octet, which is why it is highly reactive and often forms a -1 ion by gaining an electron.
CHM111 past questions and answers 12
Which of the following elements has the highest electronegativity?
- A) Sodium
- B) Chlorine
- C) Oxygen
- D) Fluorine
Answer: D) Fluorine
Explanation: Fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all elements.
CHM111 past questions and answers 13
Which of the following compounds is ionic?
- A) CO₂
- B) H₂O
- C) NaCl
- D) CH₄
Answer: C) NaCl
Explanation: NaCl is composed of a metal (Na) and a nonmetal (Cl), forming an ionic bond.
CHM111 past questions and answers 14
.What is the molecular shape of carbon dioxide (CO₂)?
- A) Linear
- B) Bent
- C) Trigonal planar
- D) Tetrahedral
Answer: A) Linear
Explanation: CO₂ has a linear shape because the two double bonds cause a linear arrangement of atoms.
CHM111 past questions and answers 16
Which factor does not affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
- A) Concentration
- B) Temperature
- C) Surface area
- D) Color
Answer: D) Color
Explanation: Color has no effect on reaction rate. Factors like concentration, temperature, and surface area do.
CHM111 past questions and answers 17
Which of the following statements about chemical equilibrium is true?
- A) At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products are equal.
- B) At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
- C) A reaction stops when equilibrium is reached.
- D) The addition of a catalyst changes the equilibrium position.
Answer: B) At equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
Explanation: At equilibrium, the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal, but the concentrations of reactants and products are generally not equal.
CHM111 past questions and answers 18
If the concentration of a reactant is increased, in which direction will the equilibrium shift?
- A) To the left
- B) To the right
- C) No change
- D) Depends on the catalyst
Answer: B) To the right
Explanation: Increasing the concentration of a reactant shifts the equilibrium toward the products (to the right) to counteract the change.
CHM111 past questions and answers 19
Which of the following is a strong acid?
- A) HCl
- B) H₂CO₃
- C) CH₃COOH
- D) NH₃
Answer: A) HCl
Explanation: HCl is a strong acid that completely dissociates in water
CHM111 past questions and answers 20
Which of the following statements about isotopes is correct?
- A) Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
- B) Isotopes of an element have the same number of neutrons but different numbers of protons.
- C) Isotopes have different chemical properties due to different numbers of neutrons.
- D) Isotopes are atoms of different elements with the same mass number.
Answer: A) Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Explanation: Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons (atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons, leading to different mass numbers. The chemical properties of isotopes are generally similar because they have the same number of electrons, which determine chemical behavior.
CHM111 past questions and answers 21
___________ is a quantitative measure of the degree of charge separation in a molecule.
- Options: (a) Molecular Geometry (b) Dipole moment (c) Lone pair (d) Charge distribution
- Answer: (b) Dipole moment
- Explanation: Dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is a vector quantity, often used to describe the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule.
CHM111 Past questions and answers 22
According to Raoult’s law, which of the following is an ideal solution?
- Options: (a) Benzene and water (b) Benzene and ethanol (c) Benzene and Toluene (d) None
- Answer: (c) Benzene and Toluene
- Explanation: An ideal solution is one where the interactions between molecules of the components are similar to the interactions between the molecules in the pure components. Benzene and toluene have similar molecular structures, which leads to similar intermolecular forces, making their mixture an ideal solution.
CHM111 past questions and answers 23
___________ is the sum total of the kinetic and potential energy of a substance.
- Options: (a) Heat (b) Internal energy (c) Enthalpy (d) Total energy
- Answer: (b) Internal energy
- Explanation: Internal energy is the total energy contained within a system, including both kinetic energy (due to the motion of particles) and potential energy (due to intermolecular forces).
CHM111 past questions and answers 24
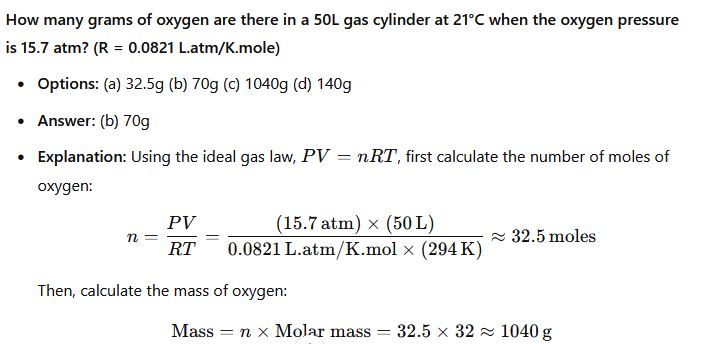
CHM111 past questions and answers 25
CHM111 past questions and answers 27
All the following may change during a chemical reaction except:
- Options: (a) The temperature of the system (b) The total number of atoms in the system (c) The density of the system (d) The total volume of the system
- Answer: (b) The total number of atoms in the system
- Explanation: In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of each element is conserved; they are rearranged but not created or destroyed. However, temperature, density, and volume can change.
CHM111 past questions and answers 28
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure exerted on the liquid is called:
- Options: (a) Boiling point (b) Triple point (c) Critical point (d) Melting point
- Answer: (a) Boiling point
- Explanation: The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.
CHM111 past questions and answers 29
The major difference existing between the three states of matter is:
- Options: (a) Degree of randomness (b) Varied shape (c) Incompressibility (d) Varied kinetic energy of the particles
- Answer: (a) Degree of randomness
- Explanation: The primary difference between solids, liquids, and gases is the degree of randomness or disorder (entropy) of the particles. Solids have the least randomness, gases have the most, and liquids are intermediate.
CHM111 past questions and answers 30
Xenon difluoride (XeF2) has a __________ molecular geometry.
- Options: (a) Tetrahedral (b) Octahedral (c) Linear (d) T-shape
- Answer: (c) Linear
- Explanation: XeF2 has a linear molecular geometry due to the arrangement of the lone pairs and bonding pairs of electrons around the central xenon atom.
CHM111 past questions and answers 31
The following are colligative properties of solutions except:
- Options: (a) Vapor pressure lowering (b) Boiling point elevation (c) Raoult’s law (d) Freezing point depression
- Answer: (c) Raoult’s law
- Explanation: Raoult’s law is not a colligative property but a principle that describes how the vapor pressure of a solution is related to the mole fraction of the solvent. Colligative properties depend on the number of solute particles in a solution.
CHM111 past questions and answers 32
Elements bordering the staircase line in the periodic table are referred to as:
- Options: (a) Transition elements (b) Metalloids (c) Halogens (d) Light elements
- Answer: (b) Metalloids
- Explanation: Metalloids have properties intermediate between metals and non-metals, and they are typically found bordering the staircase line on the periodic table.
CHM111 past questions and answers 33
The formula of magnesium nitride is:
- Options: (a) MgN (b) MgNO2 (c) Mg3N2 (d) Mg2N3
- Answer: (c) Mg3N2
- Explanation: Magnesium nitride is formed by the combination of magnesium (Mg) and nitrogen (N), with the formula Mg3N2. This indicates that three magnesium atoms combine with two nitrogen atoms.
CHM111 past questions and answers 34
Which of these is not correct?
- Options: (a) A refrigerator depends on the cooling effect of vaporization (b) Freeze-drying of food is a commercial application of sublimation (c) Solid CO2 is called dry ice because it can cool other material and does not leave any liquid residue (d) The temperature at which a pure liquid changes to a crystalline solid is called sublimation
- Answer: (d) The temperature at which a pure liquid changes to a crystalline solid is called sublimation
- Explanation: The process where a pure liquid changes to a crystalline solid is called freezing, not sublimation. Sublimation is when a solid changes directly to a gas without passing through the liquid state.
CHM111 past questions and answers 35
Molality of a solution is defined as:
- Options: (a) Moles of solvent per kilogram of solution (b) Moles of solute per kilogram of solvent (c) Moles of solute per liter of solution (d) Moles of solute per kilogram of solution
- Answer: (b) Moles of solute per kilogram of solvent
- Explanation: Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved in one kilogram of solvent.
CHM111 past questions and answers 36
Which of the following is not true of BF3 and PF3?
- Options: (a) Both have the same general formula AX3 (b) Both have the same molecular structures (c) The angle between any two P-F bonds is 120°C (d) The geometry of BF3 molecule is trigonal planar
- Answer: (b) Both have the same molecular structures
- Explanation: BF3 is trigonal planar, while PF3 has a trigonal pyramidal structure due to the presence of a lone pair on phosphorus, causing a different molecular geometry.
CHM111 past questions and answers 37
Predict the effect of increased pressure on the reaction C(s) + S₂(g) ↔ CS₂(g):
- Options: (a) More product will be formed (b) More reactant will be formed (c) There will be no change (d) The reaction is at equilibrium
- Answer: (a) More product will be formed
- Explanation: According to Le Chatelier’s principle, increasing pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer gas molecules. Here, reactants have 1 gas molecule, and products have 1 gas molecule, so pressure will not affect the equilibrium.
CHM111 past questions and answers 38
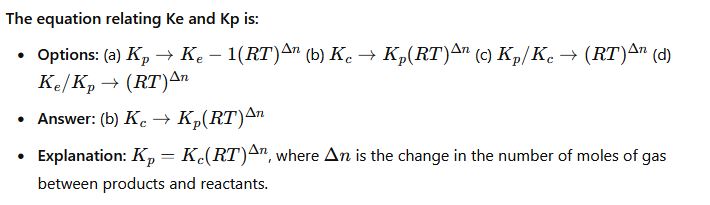
CHM111 past questions and answers 39
In which of the following compounds does the underlined element have an oxidation number of +2?
(a) Zn(OH)₄²⁻
(b) CrO₂Cl
(c) HNO₂
(d) PH₄⁺
Answer: (a) Zn(OH)₄²⁻
Explanation: In the compound Zn(OH)₄²⁻, the oxidation number of Zn is +2. The OH group has an oxidation number of -1, and since there are four OH groups, the total charge contributed by the OH groups is -4. The overall charge of the ion is -2, so Zn must have an oxidation state of +2 to balance this out.
CHM111 past questions and answers 40
A polar molecule is the one with:
(a) Lewis formula
(b) Formal charge
(c) Dipole moment
(d) Electron-dot structure
Answer: (c) Dipole moment
Explanation: A polar molecule has a dipole moment because of the uneven distribution of electrons, which results in partial charges at different ends of the molecule.
CHM111 past questions and answers 41
What is the mole fraction of glucose in a solution containing 5.68g of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) dissolved in 25.2g of water?
(a) 0.0220
(b) 0.978
(c) 1.00
(d) 0.220
Answer: (a) 0.0220
Explanation: The mole fraction is calculated by dividing the moles of glucose by the total moles of all components.
- Moles of glucose = 5.68 g / 180 g/mol = 0.0316 mol
- Moles of water = 25.2 g / 18 g/mol = 1.4 mol
- Total moles = 0.0316 + 1.4 = 1.4316 mol
- Mole fraction of glucose = 0.0316 / 1.4316 ≈ 0.022
CHM111 past questions and answers 42
In which of the following processes are covalent bonds broken?
I. Melting camphor balls
II. Boiling water
III. Boiling ethanol
IV. Dissolving iodine in water
(a) All
(b) None
(c) II and III
(d) III only
Answer: (b) None
Explanation: In all the processes listed, no covalent bonds are broken. The processes involve breaking intermolecular forces, not covalent bonds.
CHM111 past questions and answers 43
In the reaction C₃H₈O₃ + 2O₂ → 3CO₂ + 4H₂O, the coefficient of C₃H₈O₃ when the equation is balanced is:
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer: (b) 1
Explanation: The equation is already balanced, and the coefficient of C₃H₈O₃ is 1.
CHM111 past questions and answers 44
The correct electronic configuration for an element with atomic number 24 is:
(a) [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹
(b) [Ar] 3d¹ 4s²
(c) [Ar] 3d⁶ 4s¹
(d) [Ar] 3d³ 4s¹
Answer: (a) [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹
Explanation: Chromium (Cr) has an atomic number of 24. Its correct electronic configuration is [Ar] 3d⁵ 4s¹ due to the stability associated with a half-filled d-subshell.
CHM111 past questions and answers 45
Which of the species are dipoles?
I. NO₂
II. NH
III. NO₃
IV. CNS
(a) I and III
(b) II and IV
(c) II and III
(d) I and IV
Answer: (d) I and IV
Explanation: NO₂ and CNS are polar molecules with dipole moments, while NH (assuming NH₃) and NO₃⁻ are not dipoles.
CHM111 past questions and answers 46
The state reached by a reaction mixture when the rates of the forward and backward reactions have become equal is known as:
(a) Chemical kinetics
(b) Rate constant
(c) Chemical equilibrium
(d) Reaction rate
Answer: (c) Chemical equilibrium
Explanation: Chemical equilibrium is the state where the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction, and the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time.
CHM111 past questions and answers 48
Explain in terms of forces between the structural units why C₂H₅OH has a lower boiling point than NaF.
(a) H bonds in C₂H₅OH
(b) Dipole force
(c) NaF is ionic
(d) C₂H₅OH has a higher molecular mass
Answer: (c) NaF is ionic
Explanation: NaF is an ionic compound with strong ionic bonds, which require more energy to break compared to the hydrogen bonds and dipole interactions in C₂H₅OH, resulting in NaF having a higher boiling point.
CHM111 past questions and answers 50
The major discrepancy of the Rutherford atomic model corrected by Bohr’s model is that:
(a) Atoms consist of electrons and protons
(b) Electrons revolve around the nucleus continuously
(c) Electrons are higher than the nucleus of the atom
(d) The nucleus of the atom is positively charged, while the electrons are negatively charged
Answer: (b) Electrons revolve around the nucleus continuously
Explanation: Rutherford’s model could not explain why electrons do not spiral into the nucleus. Bohr’s model corrected this by introducing quantized orbits where electrons do not lose energy while revolving.
CHM111 past questions and answers 51
The bond energies in C-C, C=C, and C≡C bonds increase in the following order:
(a) C≡C < C=C < C-C
(b) C-C < C=C < C≡C
(c) C≡C > C-C > C=C
(d) C-C > C≡C > C-C
Answer: (b) C-C < C=C < C≡C
Explanation: Bond energy increases as the number of shared electron pairs increases. Triple bonds (C≡C) have the highest bond energy, followed by double bonds (C=C), and single bonds (C-C).
CHM111 past questions and answers 52
Which of the following is true about a spontaneous process at constant temperature and pressure?
(a) ΔS > T/a
(b) ΔS – ΔH/T < 0
(c) ΔS + ΔH/T < 0
(d) -ΔH/T = ΔS < 0
Answer: (b) ΔS – ΔH/T < 0
Explanation: For a spontaneous process at constant temperature and pressure, Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) must be negative. Since ΔG = ΔH – TΔS, the expression ΔS – ΔH/T < 0 describes this condition.
CHM111 past questions and answers 53
In which of the following molecules does the Sulfur atom have an expanded octet?
I. SO₂
II. SF₄
III. SO₂Cl₂
IV. SF₆
(a) I
(b) I and III
(c) II and IV
(d) II
Answer: (c) II and IV
Explanation: In SF₄ and SF₆, the sulfur atom has more than eight electrons in its valence shell, indicating an expanded octet.
CHM111 past questions and answers 54
Consider the reaction CO2(g)+C(s)↔2CO, ΔH=+172.5 KJ\Delta H = +172.5 . The forward reaction is favored by:
(a) High pressure
(b) High temperature
(c) Low temperature
(d) Low volume
Answer: (b) High temperature
Explanation: The reaction is endothermic (ΔH>0), meaning that heat is absorbed during the forward reaction. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, increasing the temperature favors the endothermic forward reaction to absorb the added heat.
CHM111 past questions and answers 55
The equation that illustrates the wave-particle duality nature of matter is:
(a) Planck’s equation
(b) Bohr’s equation
(c) De Broglie’s equation
(d) Heisenberg equation
Answer: (c) De Broglie’s equation
Explanation: De Broglie’s equation (λ=h/mv) relates the wavelength of a particle to its momentum, showing the wave-particle duality of matter.
CHM111 past questions and answers 56
Which of these is a false solution?
(a) Carbon(IV) oxide in water
(b) Oxygen in nitrogen
(c) Alkanol in water
(d) Water vapor in air
Answer: (a) Carbon(IV) oxide in water
Explanation: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) in water forms carbonic acid, and this reaction does not result in a true solution but rather a chemical equilibrium between CO₂, water, and carbonic acid.
CHM111 past questions and answers 57
When counting the electron domains around the central atom using VSEPR theory, which of the following is not considered?
(a) Non-bonding pair of electrons
(b) Single covalent bond
(c) Double covalent bond
(d) Core level electron pair
Answer: (d) Core level electron pair
Explanation: In VSEPR theory, only valence electrons are considered when determining the geometry of a molecule. Core level electrons do not participate in bonding and are therefore not counted as electron domains.
CHM111 past questions and answers 58
All the following may change during a chemical reaction except:
(a) The total number of atoms in the system
(b) The temperature of the system
(c) The density of the system
(d) The total volume of the system
Answer: (a) The total number of atoms in the system
Explanation: According to the law of conservation of mass, the total number of atoms remains constant during a chemical reaction, though their arrangement and the properties of the system may change.
CHM111 past questions and answers 59
The periodic law tells us that:
(a) Only the physical properties of the elements should vary in periodic fashion
(b) Only the chemical properties of the elements should vary in a periodic fashion
(c) Both the physical and chemical properties should vary in a periodic fashion
(d) None of the above is correct
Answer: (c) Both the physical and chemical properties should vary in a periodic fashion
Explanation: The periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
CHM111 past questions and answers 60
Which of the following elements would best not be classified as a metalloid?
(a) P
(b) Si
(c) Ge
(d) As
Answer: (a) P
Explanation: Phosphorus (P) is not a metalloid; it is classified as a nonmetal. Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), and Arsenic (As) are metalloids.
CHM111 past questions and answers 61
When arranged in order of increasing atomic number, the elements exhibit periodicity for all the following properties except:
(a) Ionization energy
(b) Atomic radii
(c) Electronic configuration
(d) Atomic masses
Answer: (d) Atomic masses
Explanation: While atomic masses generally increase with atomic number, there are exceptions due to the arrangement of isotopes. However, properties like ionization energy, atomic radii, and electronic configuration exhibit clear periodic trends.
Practice Quizzes: Test your ability
To get the most out of your study sessions, make quiz practice a regular part of your routine. Set aside a few minutes each day to tackle a quiz, and watch as your understanding deepens and your scores soar.
Remember, every quiz you take is a step closer to achieving your goals. Whether you’re preparing for an exam, enhancing your knowledge, or simply testing your understanding, practice quizzes are your gateway to success. So, take the leap—start quizzing today, and empower yourself to reach new heights!
